Efgartigimod (formerly ARGX-113) Development
Mechanism of Action
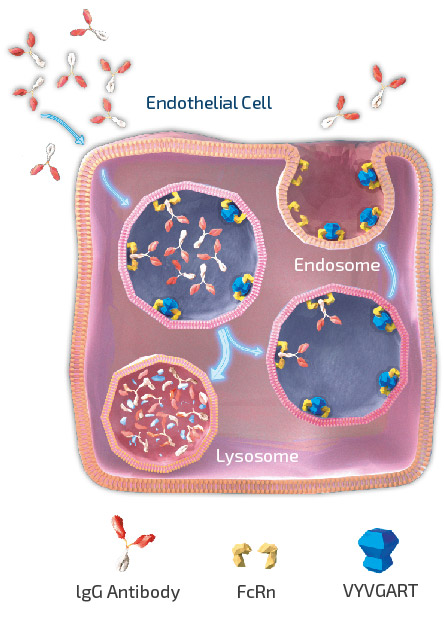
As shown in figure 3, efgartigimod is a human IgG1 Fc fragment equipped with our ABDEG mutations that is designed to target the FcRn and reduce IgG. FcRn is foundational to the immune system and functions to recycle IgG, extending its serum half-life over other Igs that are not recycled by FcRn. IgGs that bind to FcRn are rescued from lysosomal degradation. By binding to FcRn, efgartigimod can reduce IgG recycling and increase IgG degradation.
Compared to alternative immunosuppressive approaches, such as B-lymphocyte (B-cell), depleting agents, efgartigimod acts in a highly selective manner. As of the date of this Annual Report, efgartigimod has been evaluated in over 1,300 subjects with a cumulative exposure of over 1,000 patient years. Efgartigimod has been observed to significantly reduce concentrations of all IgG subtypes without decreasing levels of other Igs or human serum albumin, which is also recycled by FcRn.
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled first-in-human study of 62 healthy volunteers, efgartigimod treatment resulted in rapid and specific clearance of serum IgG levels. Single administration of efgartigimod reduced IgG levels up to 50% while multiple dosing further lowered IgGs on average by 75% from baseline. Approximately eight weeks following the last administration, IgG levels returned to baseline. Efgartigimod did not alter homeostasis of albumin or Igs other than IgG and no serious adverse events as defined by the competent authorities related to efgartigimod infusion were observed.
Based on its mechanism of action in targeting FcRn to selectively reducing IgGs, efgartigimod has the potential to address a multitude of severe autoimmune diseases where pathogenic IgGs are believed to be mediators of disease.
As of the date of this Annual Report, we continue to evaluate efgartigimod in ten autoimmune indications where significant unmet need exists despite the availability of commonly used therapies. These include gMG, CIDP and Myositis within our neurology franchise; ITP, PC-POTS and Primary SjS within our hematology and rheumatology franchise; PV, PF and BP within our dermatology franchise; and LN and MN within our nephrology franchise. In 2023, we announced our intention to expand efgartigimod into three new indications: TED, AV and AMR.
Indication Selection Strategy
We utilize the following strategy to select indications for efgartigimod:
- We first start with a strong, unifying biological rationale. The indications in our pipeline are unified in that there exists a wide range of supportive evidence that demonstrates that each is IgG-mediated. This ranges from published literature, clinical trials with currently used therapies such as intravenous Ig (IVIg), PLEX, or Rituximab, and other experiments, such as passive transfer models.
- We also look at indications where a significant clinical or commercial opportunity exists. These are disease areas where there is a significant unmet need for innovation as patients are often not well-managed by current therapies and their respective side effects. For example, steroids and ISTs are often used to treat a multitude of autoimmune diseases, but for the indications in our pipeline thus far, these have been observed to be lacking in both safety and tolerability.
- Furthermore, for each indication, there is a defined path forward with established precedent for how to run proof-of-concept and registrational clinical trials with generally accepted clinical and regulatory endpoints.
- Finally, as we work towards achieving our ‘argenx 2025’ vision, we select indications where there is a reasonable fit within our growing commercial franchises.
Formulations
Overview
We are developing two formulations of efgartigimod to address the needs of patients, physicians, and payors across indications and geographies, including IV efgartigimod (VYVGART) and the ENHANZE® (licensed from Halozyme) SC formulation.
IV (VYVGART)
We conducted a Phase 1 clinical trial in healthy volunteers to evaluate the safety, tolerability, PK, PD, and immunogenicity of single and multiple doses of efgartigimod. In the first part of the clinical trial, 30 subjects were randomized to receive a single dose of efgartigimod or placebo ranging from 0.2 mg/kg to 50 mg/kg. In the second part of the clinical trial, 32 subjects were randomized to receive MADs of efgartigimod or placebo up to a maximum of 25 mg/kg.
In the MAD part of the Phase 1 clinical trial, repeat administration of both 10 mg/kg and 25 mg/kg of efgartigimod every seven days, four doses in total, and 10 mg/kg every four days, six doses in total, was associated with a gradual reduction in levels of all four classes of IgG antibodies by 60% to 85%, with 10 mg/kg dose results shown in figure 4. For all doses in the MAD part of the Phase 1 clinical trial, we observed the reduction in circulating IgG antibody levels to persist for more than four weeks after the last dose with levels below 50% at approximately three weeks and did not return to baseline levels for more than one month. PK analysis of serum baseline levels of efgartigimod indicates that it has a half-life of approximately three to four days with no drug accumulation following subsequent weekly dosing. The prolonged activity on the levels of IgG antibodies is consistent with the mechanism of action of efgartigimod and the effect of our proprietary ABDEG technology (detailed in section “Platform Technologies”) on increasing the intracellular recycling of efgartigimod. In both the single and MAD portions, no significant reductions in IgM, IgA or serum albumin were observed.
SC – Partnership with Halozyme
In 2020, we and Halozyme expanded the existing global collaboration and license agreement that was signed in February 2019. Under the expansion, we gained the ability to access Halozyme’s ENHANZE® drug delivery technology for three additional exclusive targets upon nomination bringing the total to six potential targets under the collaboration. To date, two targets have been nominated including the human FcRn and C2.
In July 2019, we evaluated an SC formulation of efgartigimod that incorporates Halozyme’s ENHANZE® drug delivery technology in a Phase 1 clinical trial in healthy volunteers, which demonstrated retained PD profile of IV-formulated efgartigimod.
ENHANZE® has demonstrated across multiple FDA-approved products the ability to remove traditional limitations on the volume of biologics that can be delivered subcutaneously, potentially shortening drug administration time, reducing healthcare practitioner time, and offering additional flexibility and convenience for patients.
In November 2022, we announced that the FDA accepted for priority review a BLA for SC efgartigimod (1000 mg efgartigimod-PH20) for the treatment of adult patients with gMG who are AChR-AB+. The BLA has been granted a PDUFA target action date of June 20, 2023.
SC – Partnership with Elektrofi
In April 2021, we entered into a collaboration and license agreement with Elektrofi to explore Elektrofi’s high-concentration, low-volume delivery technology for efgartigimod, and up to one additional target. See section “Our Exclusive License with Elektrofi for efgartigimod” for more information.
