Sustainability Strategy
Sustainability and Our Business Model (SBM-1)
Our mission is to transform the lives of patients by translating immunology breakthroughs into novel antibody-based medicines. From the development of innovative therapies to our collaboration with stakeholders, we are committed to addressing the needs of diverse patient groups across geographical regions and prioritizing the development of treatments that make a meaningful difference in health outcomes. Additionally, we regularly engage with healthcare providers, regulators, and patient advocacy groups to ensure our efforts align with the needs of patients and contribute to global health improvements.
Our sustainability strategy emphasizes non-financial performance data and discloses metrics that offer insight into our long-term sustainability commitment and global community role. We view sustainability as a strategic enabler, driving innovation, resilience, and long-term societal impact. We are refining our approach to sustainability, with the scope of our disclosures informed by the results of our DMA. Currently, our primary focus is on establishing baseline data, which aims to lay the foundation for a comprehensive and impactful sustainability strategy that integrates long-term objectives across all aspects of our operations.
Our Business Model and Sustainability
Our business model centers on the discovery, development, and commercialization of innovative immunology therapies designed to transform the lives of patients suffering from severe autoimmune diseases. Leveraging proprietary antibody engineering technology, we have developed a robust pipeline of therapeutic candidates to address unmet medical needs globally. As of December 31, 2024, we had 1,599 employees, reflecting the significant expanse of our operations and innovation pipeline, and have total operating income of $2.3 billion.
Products and Services
For a description of our products, please refer to Section 1.1.2 “Our Medicines” of this Annual Report.
We serve a diverse range of significant markets and customer groups globally. We aim to comply with all regional regulations and market specific restrictions. Market access for our products is subject to market approval by the competent regulatory authorities of the relevant jurisdiction.
Our Value Chain
Our value chain is a structured network that encompasses our approach to 1) Research & Development (R&D) and 2) Commercial operations.
Within our value chain, R&D encompasses upstream activities such as early-stage research, the sourcing of biotechnology and raw materials. Core operations within this part of the value chain include preclinical studies, clinical trials, collaboration with external partners, such as Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs), focused on manufacturing investigational drug substances, and Contract Research Organizations (CROs), focused on drug discovery and development processes. This part of the value chain culminates in regulatory submissions that pave the way for eventual commercialization.
Commercial operations include upstream activities such as manufacturing processes to produce finished products and collaboration with our external CMOs who support bulk production, packaging, and labeling of products within our value chain. Downstream activities within this part of the value chain include global distribution, patient support programs, and the responsible management of products at the end of their lifecycle. Core operations within our value chain include sales and marketing activities that engage downstream payers.
Our Impact on Patients
Our business model, founded on discovery, development, and commercialization, leverages proprietary antibody engineering technology to create a robust pipeline of therapeutic candidates. Medicines such as VYVGART and VYVGART SC significantly improve the quality of life and functionality for autoimmune patients, benefiting both patients and healthcare providers. By prioritizing patient health and treatment efficacy, we contribute to broader social well-being and alleviate pressures on healthcare systems worldwide, underlining our commitment to stakeholder welfare.
Our Double Materiality Assessment (IRO-1, IRO-2)
Under the European Sustainability Reporting Standards regulation, companies are required to undertake a double materiality assessment (considering both impact and financial sustainability matters). In 2024, we conducted an initial double materiality analysis aligned with the CSRD and ESRS standards. This assessment aimed to identify the most pertinent environmental, social, and governance topics that could present financial risks and opportunities for argenx (outside-in perspective), while evaluating the impact of our activities on people and the environment (inside-out perspective).
Our 2024 Materiality Assessment Followed a Structured Approach:
Defining Scope and Objective of the Materiality Assessment
The initial phase involved defining our primary activities, mapping the value chain, and determining geographical scope. The following entities were subject to the materiality review:
Name of the Company |
|
Registered Office |
|
Country |
|
% Ownership |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
argenx Australia Pty Ltd |
|
Level 14, 2 Riverside Quay Melbourne VIC 3006 |
|
Australia |
|
100% |
argenx Austria Services GmbH |
|
Graben 19, 4th & 5th floor, Vienna, A-1010, Austria |
|
Austria |
|
100% |
argenx Benelux BV |
|
Industriepark-Zwijnaarde 7, 9052 Zwijnaarde, Belgium |
|
Belgium |
|
100% |
argenx BV |
|
Industriepark-Zwijnaarde 7, 9052 Zwijnaarde, Belgium |
|
Belgium |
|
100% |
argenx Canada Inc |
|
9131 Keele Street Suite A4, Vaughan, Ontario, Canada, L4K 0G7 |
|
Canada |
|
100% |
argenx France SAS |
|
Rue Camille Desmoulins 13, 92130 Issy-Les-Moulineaux, France |
|
France |
|
100% |
argenx Germany GMBH |
|
Konrad-Zuse-Platz 8, 81829 Munich, Germany |
|
Germany |
|
100% |
argenx Italy S.r.L. |
|
Largo Francesco Richini 6, 20122 Milan, Italy |
|
Italy |
|
100% |
argenx Japan KK |
|
HULIC JP Akasaka Building 2-5-8, Akasaka, Minato-ku, Tokyo, 107-0052, Japan |
|
Japan |
|
100% |
argenx Netherlands Services BV |
|
Laarderhoogtweg 25, 1101 EB Amsterdam, the Netherlands |
|
Netherlands |
|
100% |
argenx SE |
|
Laarderhoogtweg 25, 1101 EB Amsterdam, the Netherlands |
|
Netherlands |
|
100% |
argenx Spain S.L Sucursal em Portugal |
|
Palácio Sottomayor, Rua Sousa Martins, nº. 1, 1º esquerdo, 1050 217 Lisboa, Portugal |
|
Portugal |
|
100% |
argenx Spain S.L. |
|
Paseo Dela Castellana 200, Planta 8a, Oficina 819 28046 Madrid |
|
Spain |
|
100% |
argenx Switzerland SA |
|
Rue du Pré-de-la-Bichette 4, 1202 Geneva, Switzerland |
|
Switzerland |
|
100% |
argenx UK Ltd. |
|
Spaces Gerrards Cross Chalfont Park, Building 1 Gerrargs Cross, SL9 0BG, UK |
|
UK |
|
100% |
argenx US Inc. |
|
33 Arch Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02110 |
|
US |
|
100% |
OncoVerity, Inc |
|
Aurora, Colorado, United States |
|
United States |
|
50% |
To learn more about our consolidation scope, refer to “Note 30 Overview of Consolidation Scope”.
The double materiality assessment also incorporated a value chain mapping exercise, which identified the most relevant upstream and downstream activities, relationships, and sectors affecting our operations. We evaluated our Tier One suppliers and main customer base, split by geographic locations, to ensure the assessment accurately captured impacts across the value chain. Using ESRS guidelines, topics were mapped and clustered according to their relevance across the value chain, resulting in a tailored list of ESG topics for assessment that ensures compliance with CSRD requirements.
To ensure a focused assessment on high-risk activities and relationships, our value chain mapping included identifying areas where heightened risks could arise due to specific operational, business, or geographic factors. This targeted focus enables us to assess our operations and partnerships effectively, incorporating geographic and sector-specific insights to understand potential adverse impacts.
When considering the CSRD perimeter, argenx concluded that all entities fall within their direct operations. However, this scope did not include OncoVerity, as it is considered part of the value chain. argenx holds a 50% non-controlling interest in OncoVerity, which remains an unconsolidated entity. Our new subsidiaries in Portugal and Austria were incorporated after the double materiality assessment process concluded therefore, these subsidiaries were not directly considered as part of our business context for the purpose of impact, risk, and opportunity identification. However, given these new subsidiaries do not differ in their purpose it was agreed that the final material impacts, risks, and opportunities were representative of the activities of these newer subsidiaries.
Identifying Topics and Impacts, Risks, and Opportunities:
Preliminary Identification Process
We conducted an initial evaluation of our business context, encompassing operations, products, services, locations, customers, suppliers, and material inputs, to identify a preliminary list of potential sustainability matters. This evaluation was integrated with the extensive list of sustainability matters outlined in the ESRS sector-agnostic sub-topics, along with our previously established sustainability priorities. The outcome of this process is an initial compilation of potential material sustainability matters.
Stakeholder Engagement
To define material matters in the context of ESG double materiality, we employed a stakeholder engagement strategy focused on direct internal stakeholder engagement, supplemented by indirect external stakeholder engagement. Engagement methods included:
- Direct methods: Semi-structured interviews and workshops.
- Indirect methods: Desk research.
Insights were gathered from stakeholders in our key operating regions and complemented by localized analyses in specific countries. We did not include direct consultation with external stakeholders. As a proxy, however, our staff represented external groups such as suppliers, patients, and sector associations. Through engagement and dialogue with these stakeholders, our team has a detailed understanding of their views. Internal stakeholders included employees, members of our Board of Directors, and the executive team. The stakeholder groups represented by argenx employees included Human Resources, Facilities and Environment, Health and Safety, Technical Operations, Global Patient Advocacy and Policy, Legal, Compliance and Intellectual Property, Investor Relations, Global Clinical Operations, Finance, Internal Controls, Commercial team, Research & Development, Internal Audit, and Global Sourcing & Alliance Management. Below is an overview of our stakeholder engagement process, outlining the various stakeholder groups and the representative groups that conveyed their input that informed our double materiality assessment.
Stakeholder Category |
|
Stakeholder Group |
|
Stakeholder Group Representative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Affected Stakeholder |
|
Employees |
|
Human Resources and Employee Safety |
|
Local Residents/Communities |
|
Not Applicable – Desktop Research |
|
|
Manufacturers/Suppliers (CMO, CRO, Partners) |
|
Clinical Procurement |
|
|
Healthcare Community (a.o Patients, Collaborators and Patient Organizations) |
|
Patient Advocacy |
|
|
Board of Directors, CSR Steering Committee (Environmental Expert) |
|
Corporate Governance |
|
|
Shareholders/Investors |
|
Investor Relations |
|
|
Landlords |
|
Facilities and Environment, Health and Safety |
|
|
Service Providers |
|
Pre-clinical, Clinical, and Commercial |
|
|
Transporters |
|
Operations, Procurement and Supply Chain Team |
|
User of Sustainability Report |
|
Shareholders/Investors |
|
Investor Relations |
|
Rating Agencies |
|
Finance and Controls |
|
|
Authorities |
|
Government Relations |
|
|
Financial Institutions/Banks |
|
Finance and Controls |
|
|
Patients and Patient Organizations |
|
Patient Advocacy |
|
Internal Experts |
|
Finance Team |
|
Finance and Controls |
|
Human Capital Team |
|
Human Resources |
|
|
Commercial Team |
|
Commercial |
|
|
Operations, Procurement and Supply Chain Team |
|
CMC-Supply Chain |
|
|
R&D Team |
|
Science/research |
|
|
Legal and Compliance Team |
|
Legal and Compliance |
|
|
Animal Welfare |
|
Animal Welfare |
|
|
Scientific and Clinical Development Teams |
|
Scientific and Clinical Development Teams |
|
|
Privacy |
|
IT, Business Information Systems and Cybersecurity, External Counsel |
|
External Experts |
|
Consultants (PwC) |
|
PwC |
|
Doctors, Researchers |
|
Science/Research |
|
|
NGOs/Federations/Authorities |
|
Not Applicable – Desktop Research and advising from PwC |
Assessment and Due Diligence
argenx synthesized stakeholder insights and external sources – such as existing risk frameworks, corporate strategy documents, sector reports, and scientific studies – to validate and refine the list of potential impacts, risks, and opportunities. Analytical tools like a proprietary IRO tool that presents IROs derived from sector-specific SASB standards and ESRS Sustainability matters, supported the identification of sector-specific material topics. Use of this tool provided structure and orientation for the materiality analysis, guiding the assessment process. There are currently no other formalized policies that incorporate international guidelines, other than those mentioned in our Code of Conduct.
Materiality Assessment Methodology
Quantitative Scoring
Sustainability matters were prioritized through the scoring criteria aligned with the ESRS guidance:
- Impact materiality: Impacts were scored (one to five) on scale (how grave the impact is), scope (how widespread the impact is), and irremediable character (how difficult a negative impact is to remediate) with a severity score calculated as the mean of scale, scope, and irremediable character.
- Financial materiality: Risks and opportunities were scored on likelihood and potential financial impact. Risks and opportunities considered financial, operational, reputational and/or legal factors. The mean score of financial impact and likelihood was used for prioritization.
Example: The impact “inability to ensure the safety of clinical trial participants” scored five out of five for scale, three out of five for scope, and five out of five for irremediable character, yielding a severity score of 4.3.
Threshold Review
We evaluated three thresholds (three, three and a half, and four out of a possible five) to identify material IROs. The threshold of four out of five was chosen as we believe that this best represented the most material sustainability matters for argenx across environment, own workforce, consumers, and end-users and governance. Following this process, our team overseeing the materiality assessment reviewed IROs that both did and did not meet the threshold as part of the validation process. It was determined that five additional IROs that were initially below the threshold should be included as material, based on key stakeholder views on sustainability matters.
Validation and Governance
Findings were validated by argenx’s Senior Management Team and the Board of Directors to ensure alignment with strategic objectives.
Strategic Integration of Material IROs
The relationship between material IROs and argenx’s strategy and business model is fundamental to its sustainability efforts. The material IROs were tested against our existing risk management criteria and the latest corporate strategy for alignment to help position argenx to address key ESG challenges and opportunities. For any risk factors that were relevant to ESG matters and aligned with an IRO, they have been included in our Sustainability Statement if they passed the scoring threshold.
Ongoing Monitoring and Adaptation
As part of ongoing enhancement of our materiality assessment, the material IROs were further reviewed by our ESG leads, with support from internal expertise on supply chain, operations, and compliance teams, to enhance the IROs relevance to argenx’s business activities. The language was refined for conciseness and clarity. Stakeholders were re-engaged to provide feedback and validate previous scoring and justifications. This process led to modifications in the material IROs and subsequently, the ESRS topics that we are currently reporting on.
Double Materiality Assessment Result (ESRS 2 SBM-3)
As part of our double materiality assessment (which requires consideration of both impact and financial sustainability matters) that is required by the European Sustainability Reporting Standards regulation, argenx has identified several related material topics across the ESRS topics. We have described these in the following tables in accordance with the requirements of ESRS 2 SBM-3. That being so, all of our initiatives are reviewed to ensure compliance with local laws, and individual decisions are always based on merit, consistent with applicable laws.
E1 Climate Change
Sub-Topic & Sub-sub-topic |
|
Classification |
|
Material Impact, Risk, or Opportunity |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Climate Change Mitigation |
|
Negative Impact (actual) |
|
Indirect emissions from upstream and downstream activities, including manufacturing, purchased goods and services, transportation and distribution of raw materials and products (to Europe, Japan, and the USA), waste generated in operations, and end-of-life treatment of products. These processes also require substantial energy, often sourced from fossil fuels, which amplifies the carbon footprint associated with the reporting company’s supply chain. |
|
We serve a diverse range of significant markets and customers globally, with key partners located in the USA, Japan, Germany, and China. Partnerships, CROs, as well as CMOs and other key suppliers are critical to advancing argenx’s drug development pipeline. Energy used by these partners for refrigeration, heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC) and lighting is dependent on fossil-based fuels leading to GHG emissions that have a negative effect on the environment. As such, in 2024, we actively engaged with 21 suppliers leading to 35% primary GHG data. |
Climate Change Mitigation |
|
Negative Impact (actual) |
|
Direct operational emissions and energy usage from company owned sources (i.e., facilities and fleet) contribute to the negative effects of climate change. |
|
argenx’s fleet of transportation vehicles and operation of office buildings/facilities (i.e., R&D facilities) are a necessary part of our efforts in developing, commercializing, and distributing immunology therapies aimed at treating severe autoimmune diseases. However, these activities also produce emissions that are harmful for the environment. To address this, in 2024, we enhanced our GHG emissions inventory process. |
E5 Resource Use and Circular Economy
Sub-Topic & |
|
Classification |
|
Material Impact, Risk, or Opportunity |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Waste |
|
Negative Impact (actual) |
|
The disposal of single-use products, disposable medical devices, and hazardous waste (e.g., expired medications, chemical solvents, contaminated packaging, laboratory waste, and manufacturing byproducts) contributes to significant waste generation, resource depletion, and environmental and health risks when improperly managed. |
|
argenx’s work in the research and innovation phase of immunology therapies results in the disposal of single use products and disposable medical devices, contributing to waste generation. These materials are typically discarded after one use for health and safety purposes. As such, we are exploring to what extent disposable consumables (i.e., plastic) can be replaced by reusable consumables (i.e., glass). |
S1 Own Workforce
Sub-Topic & |
|
Classification |
|
Material Impact, Risk, or Opportunity |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Equal Treatment and Opportunities for All |
|
Positive Impact (actual) |
|
A positive, diverse, and inclusive work environment that ensures equal treatment of all employees–regardless of origin, gender, sexual orientation, or religion–promotes fairness, and strengthens teamwork and collaboration. |
|
argenx fosters an inclusive work environment where everyone feels safe and encouraged to contribute, regardless of employee origin, gender, sexual orientation, or religion. We strongly believe a diverse culture broadens the scope of ideas and creativity essential to developing and delivering innovative therapies to patients, while leading to better work outcomes for employees. |
Equal Treatment and Opportunities for All |
|
Positive Impact (actual) |
|
Investments in employee learning and development through training programs fosters employee well-being and prepares employees to meet future challenges while making them feel a greater sense of purpose and belonging. |
|
argenx encourages all employees to participate in a Personal Development Program aimed at building employees’ individual strengths in support of long-term career aspirations and goals. The development program focuses on empowering employees in their roles, while promoting a greater sense of purpose, belonging, and worthiness across argenx. |
S4 Consumers and End-Users
Sub-Topic & |
|
Classification |
|
Material Impact, Risk, or Opportunity |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Personal Safety of Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Negative Impact (potential) |
|
Inability to ensure the safety of clinical trial participants and patients can have severe impacts on users’ health. |
|
A key component of argenx’s business model is the discovery and development of medicinal treatments. To launch a drug successfully and safely in the market, we must test the drug by performing clinical trials. We manage our clinical trials through a combination of internal oversight and collaboration with external partners. We ensure the health and safety of clinical trial participants and patients through rigorous compliance with regulatory standards, including Good Clinical Practices (GCPs). Clinical trials undergo thorough review and approval by Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) or Ethics Committees, which assess trial design, patient safety measures, and ethical considerations. Additionally, independent Data Safety Monitoring Boards oversee trials, monitors safety data, and make recommendations to modify or halt trials if necessary. These measures help identify and address safety concerns proactively, minimizing risks to participants and maintaining the integrity of clinical trials. |
Personal Safety of Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Risk (Reputational) |
|
Risk of reputational damage from clinical trials’ or patients’ claims as a result of adverse events observed during clinical trials, including unforeseen reactions, if not appropriately addressed. |
|
A critical component of argenx’s business model is the development of medicinal treatments, which involves conducting clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy. Our trials are governed by stringent internal controls and partnerships with external stakeholders to ensure oversight and compliance. To mitigate reputational risks, we adhere to regulatory standards, including Good Clinical Practices (GCPs), to transparently report and manage adverse events. Independent monitoring bodies, such as Data Safety Monitoring Boards, assess safety data and recommend actions as needed. These measures minimize risks, uphold clinical integrity, and protect our reputation. |
Social Inclusion of Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Positive Impact (actual) |
|
Increased and better access to products and services (including through affordable pricing) can improve health and longevity for more patients. |
|
argenx’s business model prioritizes the development and delivery of innovative treatments that address unmet medical needs. The company ensures global access through contractual partnerships with healthcare systems, payors, and product distributors, supported by patient-affordability programs. These initiatives reduce financial barriers and seek to expand access to therapies, improving health outcomes and patient longevity. By reducing these barriers, we demonstrate adaptability and resilience in addressing healthcare challenges while fostering sustainable growth. |
Social Inclusion of Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Opportunity (Financial/Operation) |
|
Increased and better access to medicines through improving commercial/distribution channels and improving the affordability and pricing may lead to a growth in market capacity. |
|
argenx’s business model supports the development and distribution of innovative treatments with a focus on accessibility. The company collaborates with distribution partners, healthcare systems and payors to optimize supply chains and reduce barriers to access. Initiatives such as rebating and innovative value-based agreements coupled with market-specific patient-affordability programs enable us to reach more patients with our life changing products, in turn driving market expansion and improving global health outcomes in the rare disease space. These efforts enhance resilience by addressing access barriers while supporting sustainable growth and market capacity. |
Social Inclusion of Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Risk |
|
Off-label promotion exposes pharmaceutical companies to legal, financial, and reputational risks, inviting regulatory scrutiny and liability. |
|
argenx ensures compliance with all regulatory requirements governing the promotion of its products. Training programs and internal policies are in place to mitigate risks associated with off-label promotion. The relevant materials are reviewed to ensure alignment with approved product indications and global standards, such as those set by the FDA and EMA. Through these measures, we protect our reputation, minimize legal liabilities, and maintain stakeholder trust while reinforcing resilience against regulatory scrutiny. |
Information-Related Impacts for Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Negative Impact (potential) |
|
Misleading or inaccurate information relating to products can lead to improper use, including dangerous interactions with other medications or incorrect usage and dosage. |
|
Ensuring accurate and transparent communication of product information is integral to argenx’s business model. The company employs robust internal processes and collaborates with regulatory authorities to verify the accuracy and accessibility of all product-related materials. Compliance with global standards, such as those set by the FDA and EMA, is ensured through rigorous review processes. We also provide training for internal personnel who communicate with healthcare professionals, to ensure truthfulness and accuracy in the information they provide. |
Information-Related Impacts for Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Risk |
|
Risk of product misinformation and false claims, which can result in a loss of support from stakeholders (i.e., patients, doctors, pharmacists) and non-compliance, significant fines, and settlements. |
|
argenx’s business model emphasizes transparency and accuracy in product communication. The company has established a framework to ensure that all claims are substantiated and align with global regulatory requirements. The relevant materials undergo rigorous internal review processes to prevent misinformation and ensure compliance with standards such as FDA and EMA guidelines. These efforts protect the company from reputational damage, regulatory penalties, and financial liabilities while maintaining stakeholder trust and ensuring appropriate access to medicines. |
Information-Related Impacts for Consumers and/or End-Users |
|
Risk |
|
Exposing sensitive patient information risks fines and penalties, lawsuits, remediation costs and reputational damage |
|
Protecting sensitive patient information is integral to argenx’s operations and compliance framework. The company adheres to all applicable data privacy regulations, including the GDPR, and implements stringent internal controls, information security as well as cybersecurity measures to safeguard patient data. Regular risk assessments, incident response protocols, and employee training programs further mitigate the risk and potential impact of data breaches. These measures ensure compliance, protect stakeholder trust, and reinforce the company’s resilience against legal, financial, and reputational risks. |
G1 Business Conduct
Sub-Topic & |
|
Classification |
|
Material Impact, Risk, or Opportunity |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Corporate Culture |
|
Negative Impact (potential) |
|
Unethical practices (e.g., harassment, discrimination, corruption, fraud, safety issues) as a result of poor corporate culture. |
|
Poor corporate culture can compromise patient care, erode trust in healthcare practitioners, and negatively impact employee livelihood. As such, we prioritize and incorporate our five cultural pillars throughout the business – innovation, co-creation, empowerment, excellence, and humility. These pillars provide the foundation for a high-integrity environment where employees can operate at their fullest potential. |
Protection of Whistle-Blowers |
|
Negative Impact (potential) |
|
An inability to protect whistleblowers against retaliation prevents the identification and remediation of incidents towards employees and patients, impacting engagement, safety, and trust. |
|
Failing to protect whistleblowers against retaliation undermines employee engagement, compromises patient trust, and increases the risk of incidents going unaddressed. Employees may feel discouraged from raising concerns about potential issues, dangers or wrongdoings relating to our business, eroding our ability to sustain growth and innovation in a highly regulated and trust-dependent industry. In 2024, we updated the Global Speak-Up Policy which complies with Directive (EU (2019/1937) since its effective date. Employees are regularly trained and reminded of the Speak-Up Policy, which is also part of the onboarding package for every new employee. |
Management of Relationships with Suppliers and Payment Practices Towards Suppliers |
|
Negative Impact (potential) |
|
Poor relationships with suppliers and inconsistent payment practices (as a result of argenx failing to pay suppliers on time) may impact the reliability and consistency of suppliers activities, interfering with supply chains, affecting R&D and medical distribution to those in need of treatment. |
|
argenx utilizes third-party CMOs who act in accordance with the FDA’s current good manufacturing practices (cGMPs) for the manufacturing of drug substance and drug product. Poor relationship management with CMOs may lead to delays in delivering essential materials and medications, resulting in serious health consequences for patients. Recognizing the critical importance of supplier relationships, we take a meticulous approach when forming supplier arrangements, prioritizing direct contact over intermediaries to ensure reliability and transparency. |
Management of Relationships with Suppliers and Payment Practices Towards Suppliers |
|
Risk (Operational) |
|
Poor supplier relationship management can lead to risks such as low-quality products, supply chain disruptions, financial losses (e.g., increased costs and interest from late payments), non-compliance with supplier agreements and payment terms, and reputational damage, resulting in a loss of trust and credibility. |
|
Co-creation is at the core of argenx’s business model. As such, actively managing supplier relationships is critical to our success. Non-compliance and disruptions with suppliers can escalate costs, strain partnerships, and jeopardize our reputation and long-term strategic goals in a highly competitive market. This can pose significant challenges to our activities, potentially disrupting operational efficiency and causing reputational and financial repercussions. Recognizing the critical importance of supplier relationships, we take a meticulous approach when forming supplier arrangements, prioritizing direct contact over intermediaries to ensure reliability and transparency. |
Entity Specific
Sub-Topic & |
|
Classification |
|
Material Impact, Risk, or Opportunity |
|
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Product Quality and Safety |
|
Negative Impact (potential) |
|
Poor product quality can directly impact the effectiveness of treatments and overall health of patients. |
|
argenx is dedicated to building a foundation of loyalty and trust with its stakeholders on the safety and quality of our products. Compliance standards with various international regulatory bodies and intensive internal QA processes are key to assuring strong product quality. Product quality testing is performed on every batch of products to ensure sufficient quality control is integrated throughout the process. In addition, a full batch record review is performed to ensure the product is manufactured in line with the applicable regulatory requirements. |
Innovation and R&D |
|
Positive Impact (actual) |
|
Successful innovation helps find new treatments for current diseases and address unmet needs, allowing more patients to be treated. |
|
argenx’s goal is to deliver immunology innovations to patients that are both first-in-class and best-in-class to transform the lives of people with serious autoimmune diseases. At every step of the drug development process, we combine our leading antibody engineering capabilities with disease biology insights from collaborators to identify and develop innovative new treatments. |
Product Traceability (Counterfeit Drugs) |
|
Negative Impact (potential) |
|
A lack of product traceability and transparency can lead to counterfeit drugs or materials, endangering patient health. |
|
A lack of product traceability in the pharmaceutical value chain poses serious risks to patient safety as counterfeit drugs or materials may infiltrate the supply chain, compromising patient health. In compliance with national legislation like the United States Drug Supply Chain Security |
Stakeholder Engagement (SBM-2)
We engage with various stakeholders, including patients, healthcare providers, employees, suppliers, and investors, to integrate their needs and expectations into our strategy and business model. Currently, stakeholder engagement is managed through our business units, and through cross-functional teams and communities focused on our alliances, partnerships, healthcare professionals and patients, amongst other stakeholders. as we do not have a formal policy or dedicated function for this. While we did not directly consult external stakeholders for the double materiality assessment, their views were represented through our business units, which engage and dialogue with them.
Stakeholder |
|
Engagement |
|
Purpose |
|
Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Patients |
|
We host regular patient panels and listening sessions where patients share their experiences and challenges dealing with rare autoimmune conditions. |
|
Patient panels and listening sessions Strengthen patient communities as well as deepen our own ability to identify and address unmet clinical needs. |
|
Patients
|
Healthcare Providers |
|
We engage with healthcare providers for clinical research, advisory services and speaking engagements. |
|
Engaging with healthcare providers helps us advance research, gain expert insights, and share medical knowledge. |
|
Healthcare Providers
|
Employees |
|
Our employee communications and engagement team connect with employees through engagement sessions such as Culture Lab sessions. |
|
Employee engagement sessions foster colleague unity, gather insights to enhance employee experience, and promote our Cultural Pillars |
|
Employees
|
Suppliers |
|
Since 2024, our supply chain management team, in collaboration with an external vendor, has sent questionnaires to selected suppliers to gather emissions data. |
|
Supplier engagement Informs our GHG inventory via emissions data gathered |
|
Suppliers
|
Investors |
|
Our investor relations team regularly engages with shareholders on ESG matters |
|
Our investor engagements provide us insights into key ESG topics and responsible business practices |
|
Investors
|
ESG Governance and Oversight (GOV-1)
ESG Governance
Our governance structure is designed to provide robust oversight and strategic guidance. Our Board of Directors, our highest governance body, is a one-tier board under Dutch law. Our Board of Directors, with 90% independent members, is collectively responsible for our general affairs, including for governance and oversight with regard to sustainability matters. Given the breadth of topics covered under the umbrella of ESG, we have strategically allocated ESG oversight responsibilities across our Board of Directors’ specialized committees. The Audit and Compliance Committee holds ultimate responsibility for ensuring the integrity and design of our external sustainability reporting. Specific ESG themes are managed by designated committees, as depicted in the chart below.
The members of our Board of Directors bring extensive experience from the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, with significant expertise in developing and commercializing innovative therapies. Their strong track records in global markets, particularly in North America, Europe, and Asia, supports argenx’s strategic goals and international expansion. We prioritize a diverse and inclusive board of directors, encompassing a broad spectrum of perspectives, experiences, backgrounds, expertise, and gender. Please refer to “Section 3.2.4. Non-Executive Directors” for more information on the Board of Directors’ skills and expertise.
Pursuant to our Articles of Association, our Board of Directors has entrusted day-to-day management to the executive director, being our CEO. Our CEO leads a diverse and experienced senior management team, of which seven members report directly to our CEO, who is responsible for day-to-day management of the overall corporate strategy and the integration of sustainability matters therein. Within the senior management team, our general counsel has primary responsibility for management oversight regarding sustainability matters and helps to guide our sustainability strategy and disclosures, in addition to coordinating with the Board of Directors on sustainability work streams. ESG considerations are also part of the agenda of our Global Risk Management and ESG Committee.
In light of new ESG legislation, such as the EU CSRD, the Board of Directors, the Audit and Compliance Committee, and senior management have discussed how to best prepare argenx for these changes. Consistent with our outsourcing model to supplement our internal team with partners who bring unique expertise and/or fill resource capacity gaps, it was concluded that we would hire highly experienced external consultants and advisors to supplement capacity and fill any gaps in sustainability expertise. This collaboration with external sustainability consultants enhances our governance framework. As such, while leveraging internal knowledge of social responsibility and governance best practices, we engage with external advisors for environmental regulation expertise. By leveraging both internal and external expertise, we aim to stay abreast of the latest trends and best practices, effectively overseeing and advancing our sustainability initiatives.
Employees are not formally represented within the administrative, management, and supervisory bodies. Nevertheless, regular meetings, feedback sessions, and representation in committees help to ensure that their voices are heard and considered in decision-making processes. This approach aims to foster an environment where all stakeholders can contribute to the company’s approach to sustainability.
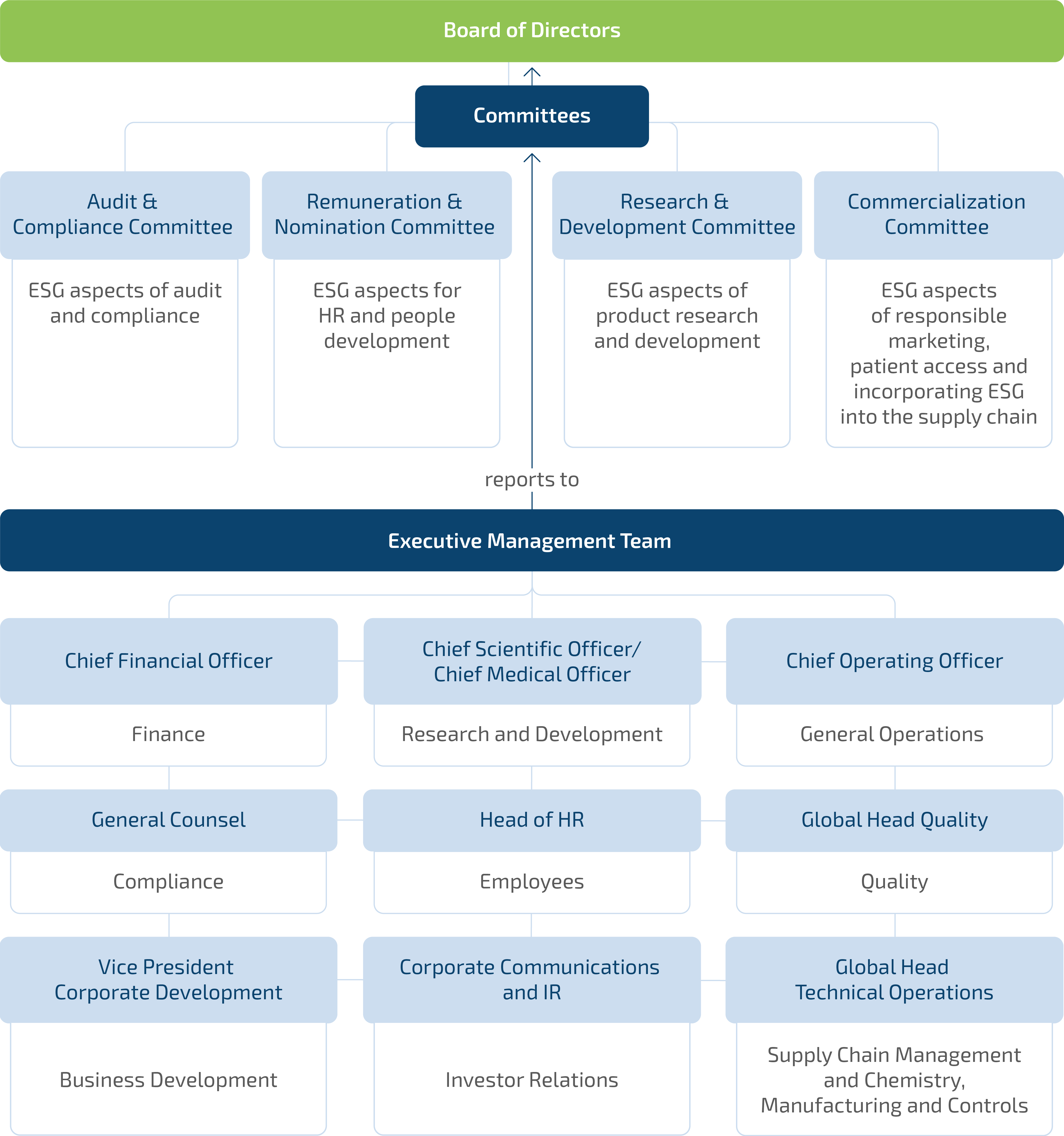
Management of Material Risks, Impacts and Opportunities by Administrative, Management and Supervisory Bodies (GOV-1, GOV-2)
In 2024, our senior management team provided quarterly updates and reports during scheduled Board of Directors meetings, ensuring that the Board of Directors and the Audit and Compliance Committee were informed of the progress on the journey towards CSRD compliance. Generally speaking, the Board of Directors and the Audit and Compliance Committee’s agenda contains topics that directly or indirectly relate to our material impacts, risks, opportunities. Key material impacts, risks, and opportunities addressed during 2024 included regulatory compliance, corporate culture, scientific innovation and affordability and pricing.
Our Board of Directors has industry expertise and knowledge, enabling effective oversight and guidance of ethical business practices. The Board of Directors in general, and the Audit and Compliance Committee specifically, have significant experience in developing and implementing compliance frameworks, monitoring anti-corruption and bribery measures, and ensuring adherence to international regulatory standards. The Audit and Compliance Committee actively collaborates with the Ethics & Compliance function to support the organization’s integrity framework. As part of the company’s Code of Conduct and Business Ethics, the Board of Directors receives quarterly updates on anti-bribery and anti-corruption matters and other compliance-related topics. This close alignment with Compliance aims to ensure that emerging risks and opportunities in business conduct are effectively addressed.
To learn more about our Board of Directors, see Section 3.2.4 “Non-Executive Directors”.
Integration of Sustainability-Related Performance in Incentive Schemes (GOV-3)
In 2024, the short-term and long-term incentive compensation for our Board of Directors and senior management did not include performance metrics specifically tied to sustainability performance.
Due Diligence (GOV-4)
In 2024, we continued to build/enhance our due diligence process within our sustainability framework to manage ESG risks and opportunities, aligning with the ESRS requirements. The double materiality assessment has been documented and reviewed by the Risk Management Committee and validated by the Audit and Compliance Committee and the Board.
Risk Management and Internal Controls Over Sustainability Reporting (GOV-5)
In 2024, we improved our risk management for sustainability reporting and have identified several main risks categories, including regulatory, and legal and compliance. To address this, we have enhanced our sustainability reporting framework by establishing an internal team and engaging external experts. In this first year of CSRD reporting, we have built systems and tools to ensure our reporting is thorough and accurate. We are committed to continuous improvement and will implement measures to address any identified inefficiencies in the future.
